Environmental Nutrition at LLUSPH
Environmental Nutrition is currently the focus of an interdisciplinary academic research group at the School of Public Health, Loma Linda University. The information on our website is relevant to students, researchers, not for profit organizations and other interested groups.
What is environmental nutrition?
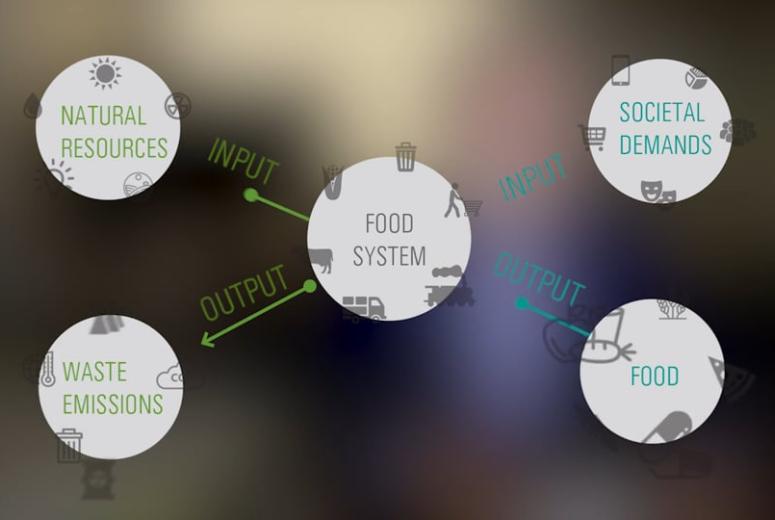
Environmental Nutrition emerged from a recognition that the complex interactions within the food system related to health and environment need to be considered simultaneously. Environmental Nutrition goes beyond the scope of current discussions on sustainable diets and systematically considers the interrelationships within food systems to necessarily incorporate a complete understanding. Nourishing a growing population while balancing what the Earth can provide and absorb is increasingly recognized as a major global challenge. The conventional food system threatens our health and overall well-being with increased air and water pollution, toxic chemical exposure, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, soil erosion, climate change inducing greenhouse gas emissions, and loss of biodiversity. Widely held consensus among medical and public health professionals finds that today’s typical ‘diet of affluence’ contributes to a range of costly health problems, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline and dementia, other neurodegenerative disorders, and various kinds of cancer. Environmental nutrition, therefore, is a useful tool for critically analyzing the wide-reaching environmental, social, and health impacts of industrial agriculture.
Examining the interrelationships between our food choices, our environment and our health.
What are sustainable diets?
By definition, a ‘sustainable’ diet should use resources without exhausting or destroying them, and hence should be able to be sustained in the long term. This includes staying within the Earth’s biophysical capacity, i.e. what the planet can sustain in terms of resource provision and absorption of wastes, including greenhouse gas emissions. The growing body of research on sustainable diets has been recognized by a variety of international bodies including the United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). The FAO define sustainable diets as “those diets with low environmental impacts which contribute to food and nutrition security and to healthy life for present and future generations. Sustainable diets are protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems, culturally acceptable, accessible, economically fair and affordable; nutritionally adequate, safe and healthy; while optimizing natural and human resources.” The food system is currently a major contributor to severe environmental problems, such as biodiversity loss and climate change. This contribution is envisaged to increase, given the global shift in food consumption patterns towards the ‘western’ palette of high animal products. Addressing consumption patterns, food waste and resource intensive methods of agricultural production are considered crucial for enabling wide scale adoption of sustainable diets.
Published by Lead Researcher

We are delighted to share the publication of Dr. Sabaté’s book Environmental Nutrition: Connecting Health and Nutrition with Environmentally Sustainable Diets. It is available to purchase. Environmental Nutrition explores the interrelatedness of diet, environmental sustainability, and human health, as well as potential solutions to these global challenges. Sixteen chapters cover the background and challenges we face to find a sustainable food system that can feed a growing population while protecting the environment we must share. Contributors include top environmental and nutrition scientist from around the globe. Click on the book name above to see your buying options at Amazon.